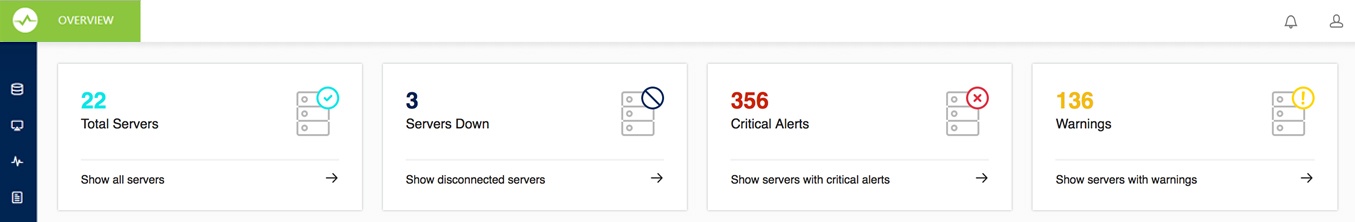
At this point, you should have SQL DM for MySQL installed and configured on a Linux or Windows server and one or more servers running MySQL that you have configured to provide monitoring data to SQL DM for MySQL. However, in order to get SQL DM for MySQL to access that data, you need to register the server with the application.
A single instance of SQL DM for MySQL can monitor hundreds of MySQL database servers. With tagging, you can categorize them into logical groups, ensuring that they're easier to keep track of and identify. During the Trial period, you can register up to 1000 MySQL servers, after which you'll need to purchase a license.
| For more information on licenses and pricing, see |
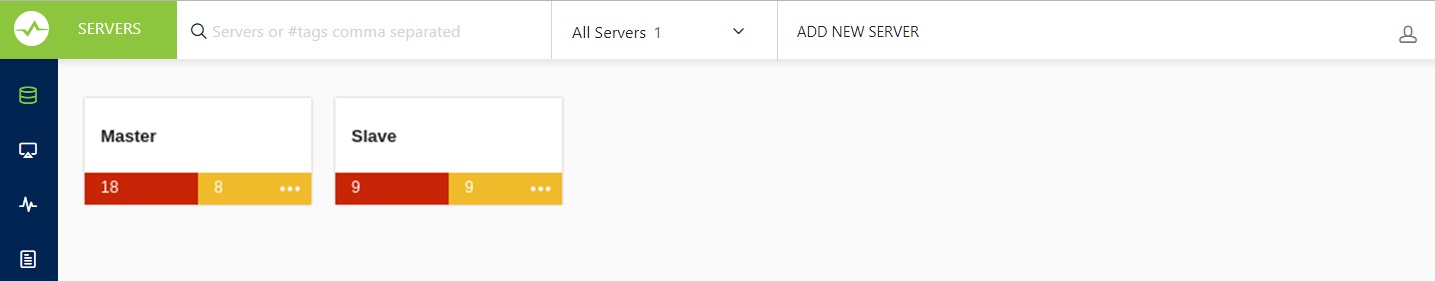
The web interface for SQL DM for MySQL provides a convenient form for adding new MySQL database servers to monitor. The link to this form is found on the Servers tab. To get there, click the Servers icon on the dock.
On the Servers tab, click the Add New Server link at the top of the page:
Clicking this link opens an overlay form which you can use to configure a new server for SQL DM for MySQL.
For general information, you need to provide a name, the IP address or domain name, port number for the MySQL host, the username, and password for the SQL DM for MySQL user on the database. Also, you have the option of setting tags to group different servers together, and setting the connection type (direct, SSH tunneling, or SSL encryption).

When you finish configuring the new MySQL server, click Save.
SQL DM for MySQL now collects data on the new server. You can view its state, compare its configuration to another servers, and much much more.