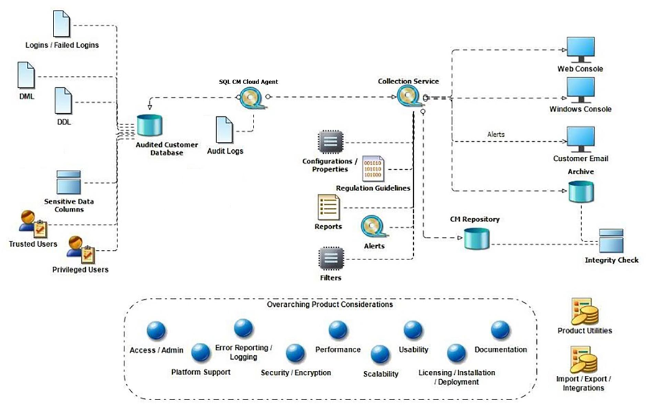
IDERA SQL Compliance Manager consists of a light, unobtrusive architecture that efficiently runs in your SQL Server environment with minimal configuration. All SQL Compliance Manager components run outside and separate from SQL Server processes. SQL Compliance Manager does not add to or modify your native SQL Server files or services.
Architecture
SQL Compliance Manager provides a robust, easy-to-use SQL Server audit and reporting solution. Behind a friendly user interface, SQL Compliance Manager offers a unique, loosely coupled architecture that is both flexible and extremely powerful. As a result, SQL Compliance Manager fits your environment, no matter how simple or complex.
The following diagram illustrates the components of the SQL Compliance Manager architecture.
Management Console
The Management Console is a centralized, intuitive user interface that allows you to easily and quickly modify audit settings, monitor events, and report on audit data. This user interface also provides the following information:
- Real-time status of audited SQL Server instances
- SQL Server login permissions
- Detailed logging of change activity
- Track and prove continual compliance using reports
Repository databases
The SQL Compliance Manager Repository is the central Repository that tracks:
- SQLcompliance configurations, such as audit settings, server registrations, and console security
- Audited SQL Server events
- Alert messages
- SQL Compliance Manager Agent activity
The Repository consists of the following databases. For more information, see How auditing works.
| Repository Database Name | Description |
|---|---|
| SQLcompliance | Stores alert messages, audit settings, SQL Compliance Manager Agent events, Activity Report Card statistics, and other SQL Compliance Manager configurations. |
| SQLcompliance.Processing | Stores processing event data received from the SQL Compliance Manager Agent. |
| SQLcompliance.Instance | Stores processed events collected from a registered instance. |
| SQLcompliance.Instance_Time_Partition | Stores archived events collected from a registered instance. |
Collection Server
The Collection Server processes trace files received from the SQL Compliance Manager Agent, stores audit data in the events and archive databases, and sends audit setting updates to the SQL Compliance Manager Agent. The Collection Server runs under the Collection Service account. By default, the Collection Server communicates with the Agents every five minutes (heartbeat) to write processed audit data to the event databases associated with the registered SQL Server instances.
SQLcompliance Agent
The SQL Compliance Manager Agent gathers SQL Server events written to the SQL trace, caching these audited events in trace files. By default, the SQLcompliance Agent calls the Collection Server every five minutes (heartbeat) to receive audit setting updates and sends trace files for processing every two minutes. The SQL Compliance Agent runs under the SQL Compliance Agent Service account. For more information, see How the SQL Compliance Manager Agent works.
SQLcompliance Cloud Agent
SQL Compliance Manager 6.0 and above support remote auditing on SQL servers on EC2, allowing users to audit instances on their Amazon EC2 Servers using the SQL CM Agent. Auditing with the Cloud Agent service, except for XEvents, Trace Files, and Before and After data, offers all the functionalities covered by the SQL CM Agent. Once the audit is complete, all data is transferred from the Cloud Agent to the Collection Service for the real-time status of your audited SQL Server instances. Users can take advantage of the improved architecture that allows registering RDS instances with the Cloud Agent Service. For more information, see How the SQL Compliance Manager Cloud Agent works
Sensitive Column auditing is supported by SQL Compliance Manager Agent 3.5 or later. To use this feature, please ensure you upgrade your agent to at least version 3.5.
Command line interface
The command line interface (CLI) provides an interface for third-party tools so you can automate and schedule regular tasks, such as audit data archival and grooming, and perform diagnostic tasks. You can also perform integrity checks through the CLI.
The CLI supports the following operations.
| CLI Operations | Description |
|---|---|
| agentsettings | Lists the SQL Compliance Manager Agent's settings on a specific SQL Server instance. |
| archive | Archives audited events collected for registered SQL Server instances. |
| auditdatabase | Enables auditing on a new database, allowing to specify either a regulation guideline or a custom audit template. |
| checkintegrity | Verifies the integrity of audited events collected for a specific registered SQL Server instance. |
| collect | Collects trace data from the agent. |
| groom | Deletes audited events older than a specified age. |
| help | Displays the CLI Help. |
| listtriggers | Lists the CLR triggers for DML auditing on a specific registered SQL Server instance. |
| registerinstance | Registers a new SQL Server instance and applies audit settings. |
| removetriggers | Removes the CLR triggers from the subscriber table on the specific SQL Server instance. |
| serversettings | Lists the settings for the Collection Server. |
| timezones | Displays the time zones recognized by the computer hosting the Collection Server. |
| updateindex | Applies optimized Repository index configurations to existing events and archive databases. |
Trace files and the trace directory
Trace files contain audited SQL Server events collected by the SQL Compliance Manager Agent. The SQL Compliance Manager Agent stores these temporary files in a secure directory on the audited SQL Server instance. When the set directory size threshold is reached, the SQL Compliance Manager Agent stops the SQL trace until the trace files are sent to the Collection Server for processing. The trace file is cycled when the set file size threshold is met. You can configure the SQL Compliance Manager Agent trace file directory location and how the Compliance Manager Agent manages these files, such as how often the agent sends trace files to the Collection Server. For more information, see How the SQL Compliance Manager Agent works.