Page History
...
The color of the index entries in the Collect and Create Indexes table is interpreted as follows:
| Text Color | Interpretation |
|---|---|
| Index is used in the query. | |
| Index is usable but not used by the current execution path. | |
| This index is missing. SQL Query Tuner recommends that you create this index. | |
| This index exists on the table but not usable in this query as it is written. |
| Anchor | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Joins are represented with connecting lines between nodes. You can move tables in the diagram by clicking and dragging them to the desired location. The position of the connecting lines is automatically adjusted. The following describes when a particular type of connecting line is used and the default positioning of the line.
| Connecting Lines | When Used |
|---|---|
| One-to-One join relationships are graphed horizontally using blue lines. For more information, see One-to-One Join. | |
| One-to-Many join relationships are graphed with the many table above the one table. For more information, see One-to-Many Join. | |
| Cartesian Join shows the table highlighted in red with no connectors to indicate that it is joined in via a Cartesian join. For more information, see Cartesian Join. | |
| Many-to-Many Join relationships are connected by a red line and the relative location is not restricted. For more information, see Many-to-Many Join. | |
| Indirect Relationship. For more information, see Indirect Relationship. | |
| Outer Join. For more information, see Outer Join. | |
| Unique. For more information, see Unique. | |
Not Exists and Not in relationship lines connect the subquery to the table being queried. Notice that when you click this relationship line, the SQL text creating the relationship is also selected. For more information, see Not In or Not Exists Join. | |
Exists and In relationship lines connect the subquery to the table being queried. Notice that when you click this relationship line, the SQL text creating the relationship is also selected. For more information, see In or Exists Join. |
| Anchor | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
...
The following SQL contains a nest IN subquery (shown in bold text) that is graphically represented with the Subquery summary icon and the IN join.
SELECT
cs.customerid, cs.firstname, cs.lastname,
mr.rentalid, mr.duedate, mr.totalcharge, ri.itemnumber
FROM
(
...
SELECT c1.customerid, c1.firstname, c1.lastname, c1.phone
FROM MOVIES.
...
customer c1
WHERE EXISTS (SELECT NULL) cs, (FROM MOVIES.customer c2
WHERE c1.customerid <>c2.customerid AND c1.lastname=c2.lastname AND c1.phone BETWEEN 0 AND 9999569900)
SELECT
customerid, rentalid, duedate, totalcharge, rentaldate
FROM MOVIES.movierental
WHERE totalcharge > 10
)
mr, MOVIES.rentalitem ri
WHERE
LENGTH (cs.lastname) = 10 AND
- 1 < cs.customerid AND ROUND (ri.rentalid) > 10 AND
TRUNC (ri.itemnumber) > 1 AND
mr.totalcharge > ( SELECT AVG (totalcharge) FROM MOVIES.movierental WHERE TOTALCHARGE >= 40) AND
ri.moviecopyid NOT IN ( SELECT mc.moviecopyid FROM MOVIES.moviecopy mc WHERE
mc.copyformat = 'vhs' AND
mc.copycondition = 'new' AND
mc.movieid IN (SELECT mt.movieid
FROM MOVIES.movietitle mt
WHERE mt.year < 1990 AND mt.rating IN ('pg', 'r') AND
mt.categoryid IN (SELECT
mc.categoryid
MOVIES.moviecategory mc
FROM WHERE
mc.rentalprice = (SELECT MAX (rentalprice) FROM MOVIES.moviecategory
WHERE categoryid = mc.categoryid))) ) AND
mr.CUSTOMERID = cs.CUSTOMERID AND
ri.RENTALID = rnr.RENTALID
!worddavd8988236c1412be99b1df02ab6a22dec.png|height=60,width=94!Graphically, this would display as the following when the MOVIECOPY (MC) subquery is expanded:
:' ... .. ...........
• ... 1.. .
;. !ill It< ) i
'•
fi} 1\10\t lER EN T Al
OUTER JOINAnchor outer outer
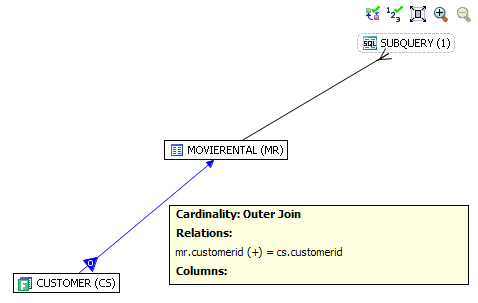
The bold SQL predicate in the statement below defines the outer join between customer and movierental.
select cs.*
from MOVIES.customer cs, MOVIES.movierental mr
where
length (cs.lastname) = 8 and cs.zip > 75062 and
1 < cs.customerid + 2 and
cs.phone between 9625569900 and 9999569900 and mr.rentalid = ( select max (ri.rentalid)
from MOVIES.rentalitem ri, MOVIES.moviecopy mc
where
ri.itemnumber > 1 and mc.moviecopyid = 700) and
mr.customerid= cs.customerid ;
The following screen shot illustrates how the outer join is displayed in the VST diagram.
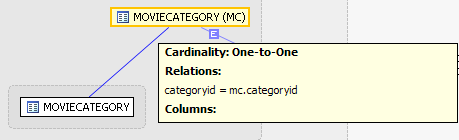
UNIQUEAnchor unique unique
The subquery below illustrates a unique relationship between two primary keys.
...select max (rentalprice) from MOVIES.moviecategory where categoryid = mc.categoryid...
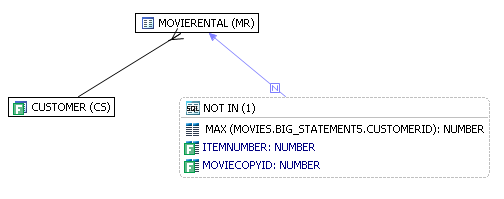
NOT IN OR NOT EXISTS JOINAnchor notexists notexists
The following SQL contains a NOT IN subquery (shown in bold below) that is graphically represented with the Subquery summary icon and the NOT IN join.
SELECT CS.* FROM
MOVIES.CUSTOMER CS, MOVIES.MOVIERENTAL MR
WHERE
CS.ZIP > '75062' AND
MR.RENTALID NOT IN ( SELECT MAX (MOVIES.BIG_STATEMENT5.CUSTOMERID) FROM
MOVIES.RENTALITEM RI, MOVIES.MOVIECOPY MC, MOVIES.BIG_STATEMENT5
WHERE RI.ITEMNUMBER > 1 AND
MC.MOVIECOPYID = 700 ) AND MR.CUSTOMERID = CS.CUSTOMERID;
Graphically, this statement would look like this:
VIEWING OBJECT SQL
Hover over the name of an object to view the object SQL as shown in the diagram below.
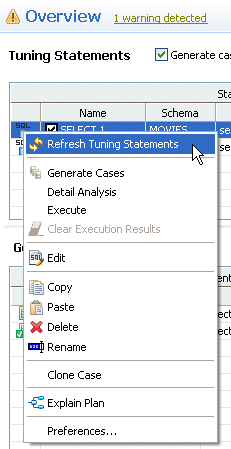
REFRESHING TUNING STATEMENTS
At times you may see an error on the Overview page, which when you mouse over it, indicates that the tuning statements are out of sync and need to be refreshed. This can happen, for example, if you tune a statement, then delete it, and insert another SQL query for tuning.
To refresh the tuning statements
In the Tuning Statements area of the Overview tab, right-click the tuning statement and select Refresh Tuning Statements.
REFRESHING THE VST DIAGRAM
There are two refresh options available: Refresh and Refresh All. Click the Refresh list as shown below to gain access to these options.
• Refresh: Regenerates the Analysis tab including the VST diagram. Any changes made on the tab are reflected in the diagram.
• Full Refresh: Re-caches all objects used in (or related to) the query, then regenerates the Analysis tab including the VST diagram. This option is typically used when the underlying objects have been recently changed.