Page History
...
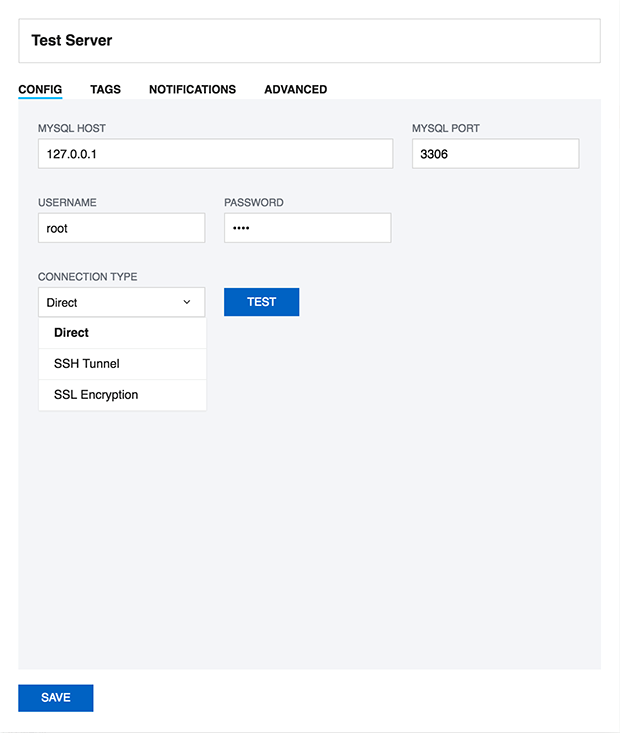
First you must register the MySQL servers that to which SQL DM for MySQL shall connect connects to. For every server you specify here, an embedded database will be is created. SQL DM for MySQL will connect connects to those servers , to retrieve and store information from that server.
For a Direct connection, just enter the connection information as you would do from any client.
To retrieve system information (CPU, memory load etc.) you will also need to give the information required to create a remote command shell (Linux) from the server machine on which SQL DM for MySQL is running.
...
SQL DM for MySQL can send and receive encrypted authentication information as well as monitoring monitored data from MySQL using SSH tunneling. Also, it will often be is possible to connect to MySQL with SSH tunneling even if the MySQL port (normally 3306) is blocked by a firewall or if users are not allowed to connect from remote hosts. An operating system user is required so that SQL DM for MySQL SSH client functionalities can use this user to connect to the SSHD daemon on the server.
...
If your MySQL server is running in the same system M1, you can choose "localhost", "127.0.0.1" or the IP address of MySQL server which M1 can see.
SSH will listen on a specified port on the client machine, encrypt the data it receives, and forward it to the remote SSH host on port 22 (the SSH protocol port). The remote SSH host will then decrypt decrypts the data and forward forwards it to the MySQL server. The SSH host and the MySQL server do not have to be on separate machines, but separate SSH and MySQL servers are supported.
...
To create a SSH connection you will be asked forneed the following:
- SSH Host: Host of the machine on which SSH server is running.
- SSH Port: Port on which SSH server is listening. By default, it is 22.
- SSH Username: Username to access the SSH server (Note: not the MySQL server).
...
- If you have specified authentication type as Key - You should note that SQL DM for MySQL only supports ''OpenSSH standard key format'' for key based authentication in SSH connections.
- Private Key: Paste the content of your private key file. Again, don’t do not specify the path to your private key file.
- Passphrase: Enter the passphrase for your private key file (if any). This can be left blank, if no passphrase was given for the private key.
...
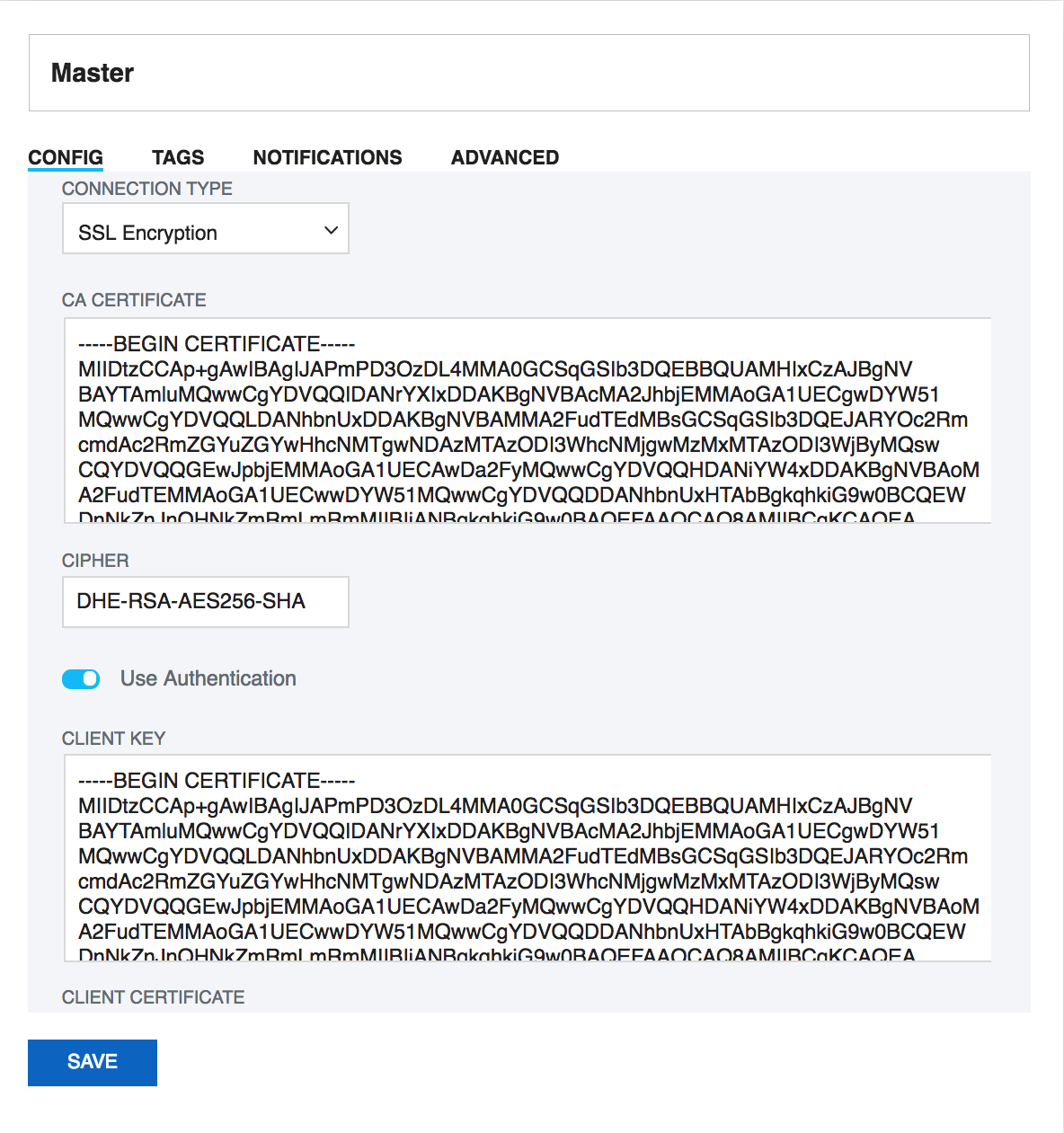
- Client Key: Private key of the client that is needed for encryption.
- Client Certificate: The client certificate.
| Scroll pdf ignore | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
WebsiteNewtabfooter |
| Products | Buy | Support | Community | About Us | Resources | Legal
Newtabfooter |
Newtabfooter |
Newtabfooter |
Newtabfooter |
Newtabfooter |
Newtabfooter |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Newtabfooter | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|