Page History
...
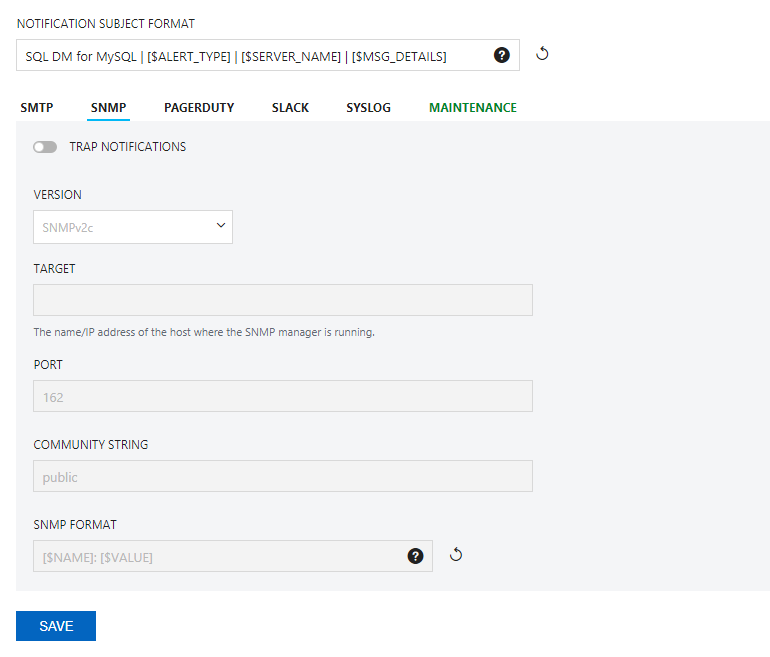
- Version: SQL DM for MySQL supports 2 types of SNMP versions: SNMPv1 and SNMPV2c. You can select the trap type from this drop down.
- Target: Type in the name or IP address of the host to which you want SQL DM for MySQL to direct traps.
- Port: Enter the destination port here; by default, it is 162. This is the port where your SNMP Manager (or Client) listens for traps.
- Community string: The read/write community string helps classify your SNMP operations. By default, SQL DM for MySQL sets it to Public, but you can change to whatever suits your need.
- SNMP Format: Specify SNMP trap format e.g. [$NAME]:[$VALUE].
- Enable status traps: Status traps are sent when SQL DM for MySQL is starting up to indicate just that. If you want to be informed of when SQL DM for MySQL is starting up, select Yes.
- Use the remote MySQL Server host IP as the SNMP trap agent address for Monitor traps: Check this option if you want the sender IP of the traps sent by SQL DM for MySQL to be that of the host where the monitored MySQL server is running, instead of the host where SQL DM for MySQL is running. This only affects the Monitor traps sent by SQL DM for MySQL.
- Clicking the Send Test Trap, results in sending a status trap to the target and port specified, containing a string that indicates that this is a test trap.
- To have your SNMP client decode the arcane digits identifying a trap, you need to load SQL DM for MySQL’s Management Information Base (MIB)s into your SNMP client. The MIB file is available in the installation directory of SQL DM for MySQL. You can also download the file from the link provided in SQL DM for MySQL browser interface.
Note more information on types of Traps:
...