This section provides information on how to configure the WhereScape CICD Enablement Pack on both Developer and Deployment Machines.
The following technologies should be in place before following the configuration setup for all Development and Deployment machines:
Environment Configuration
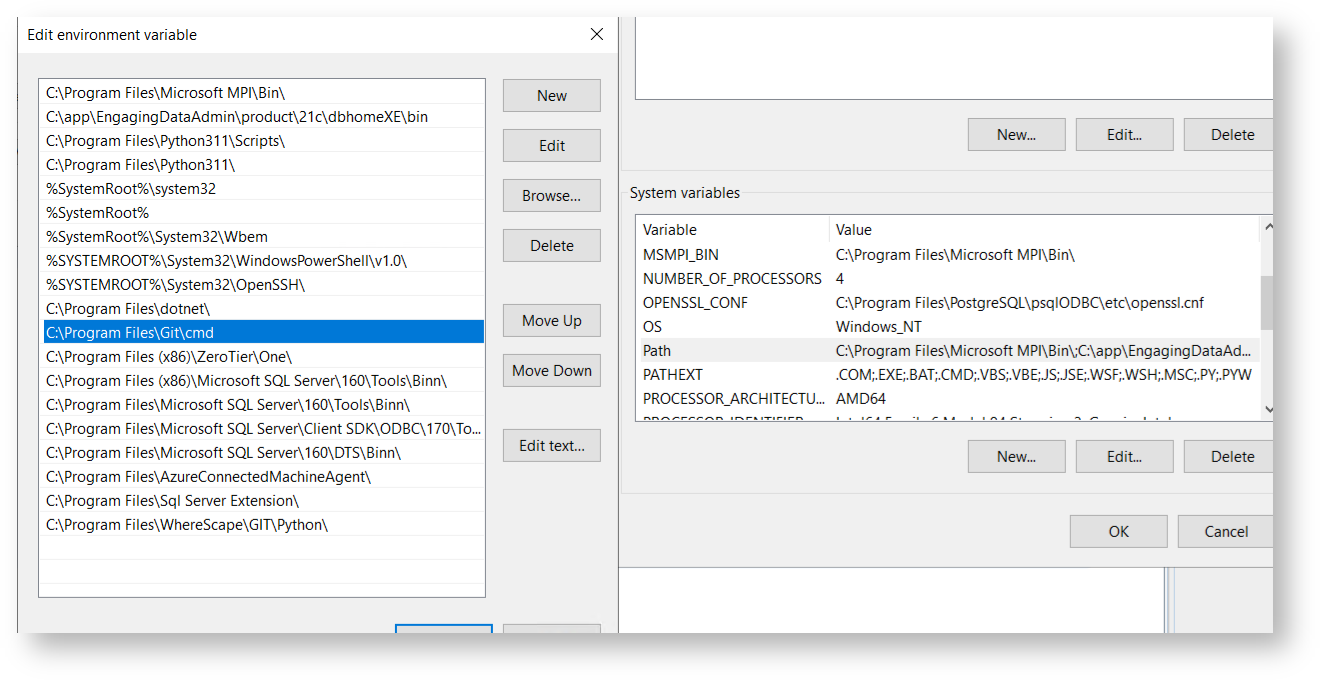
Ensure that the system-wide PATH environment variable includes the path to the GIT CMD executable (e.g. "C:\Program Files\Git\cmd"):

Make sure the following user-level PATH entries exist:

You may need to add Proxy authentication, to enable access to the API for Personal Access token authentication:

If the shortcut is not created automatically, you can manually create one by navigating to the installation directory and right-clicking the executable. |
You may need administrator rights to complete the installation. |
This section describes how the workflow should be configured on the Development machine.
All developer machines must have the same configuration and installation steps in the Prerequisite section. These processes have been deployed and tested on the following Development machine types:
Downloads for the latest versions of WhereScape 3D & RED, along with installation guides, can be found here: https://www1.wherescape.com/support/software-downloads-documentation/
With WhereScape 3D and RED, the metadata is stored in a repository within a PostgreSQL database. The installation process will check and update the PostgreSQL database structure, ensuring that the structure matches the software update requirements.
If there are any updates to WhereScape 3D or RED in the future, please follow the installation instructions. Update the software to ALL Developer Machines and the shared repository outside of business hours to remove the risk of corrupting the repository. Always back up the repository before you start the software update. |
Ensure that the Azkaban service has been installed and started. This can be found in the services of the Virtual Machine.
Server: User-specified
Port: User-specified
Database: wsred_[Name of GIT repository][_$ENVIRONMENT$]_$DEVELOPER$
Username: User-specified
Password: User-specified
It is a prerequisite of the GIT Enablement Pack that the user has already set up an ODBC connection for both source and target databases. The naming conventions for the ODBCs need to be consistent across all users. |
Please note, if the user would like to explore the local PostgreSQL server, they will need to connect pgAdmin UI to the local wsMetaServer (WhereScape’s PostgreSQL server installed as part of WhereScape 3d). Use the Server details above to achieve this. |
Each end user will require access to the shared GIT repository. The end user’s credentials are used when pushing commits (during the WhereScape 3D & RED workflows).
Repository Name: User-supplied
Repository local path: %USERPROFILE%\Git\[Name of Repo]
The location of the local GIT repository can be changed within the User Config file. |
The workflow is designed to push individual files to the repository. However, if there are any errors when pushing to Git, please use a GIT GUI to manage conflicts. |
This section describes how to setup a deployment machine that can be used to create a CICD workflow to publish changes into a selected target database.
This enablement pack will trigger the WST deployment process via the command line. For further information on this, please refer to the WhereScape RED help guide.
All deployment machines must have the same configuration and installation steps in the prerequisites section.
To deploy the application to target environments, the below link provides instructions to configure a self-hosted runner as a service.
For more information consult the documentation here: GitHub - Hosting your Own Runners
It is recommended that you consider this before continuing or selecting the option.
This will enable the machine to be configured specifically for that runner and the required deployment tasks. For example, you may require specific software for that runner.
However, this will create a more complex environment to support and may also be more cost-inefficient.
This will enable the runners to utilize the setup of the deployment machine environment configuration for many runners.
When creating the agents or runners, include the solution name within the name of the runner, for example: [Machine Name]_[Project]_[Environment]
Your selected option depends on how complex you wish to make the environment. Having one deployment machine with many runners may be simpler to support and more cost-effective in the long run. However, this may create an environmental configuration restriction that may prevent you from scaling the solution in the future.
Also, you should understand the CPU requirements for deployment, as the deployment machine will use the CPU while executing the deployment to the target platform. This is only a consideration if you have many runners on a single deployment machine and, therefore, parallel tasks taking place that are trying to consume the CPU from that deployment machine.
When you run the WhereScape CICD Enablement Pack all workflow logs will automatically be created within the following folder:
%USERPROFILE%\WhereScape\GIT\Logs
Whenever you run a workflow task, the user can access these logs to see information relating to them.
If this folder is used, please ensure that the user profiles have read/write permissions. Failure to do this will prevent the workflow tasks from working correctly. |
When you create a repository in WhereScape 3D or RED, its name is automatically linked to the name of your GIT repository.
If you rename your WhereScape 3D or RED repository later, it will break the connection to your GIT repository and the CI/CD configuration files. This can cause issues with version control and automated deployments. |
Don’t create new repositories in WhereScape 3D that point to existing ones already set up for CI/CD.
Firewall Rules and Proxy Configuration
Please note, that some organisations using proxy servers, may need to run the following git command:
|
Getting Started with WhereScape CICD Enablement Pack